Hard hammer
-
Heavily ground platforms
-
Alar platform detachments
-
Tendency for step and hinge termination, especially with copper
-
Continuous platforms
-
Thick, wedge-shaped flakes
-
Distinct ripple marks
-
Tendency for hinge termination
-
Overshots are unusual with thin flakes
-
Impacts offset from the core face plane
-
Generally responsible for the thickest flakes
Soft hammer
-
Arcuate platform detachment
-
Light platform strengthening
-
Isolated platforms
-
Oval flake shape at late stage
-
Subdued ripple marks
-
Overshots are easily controlled
Indirect percussion (by rocker)![]()
-
Acute platform edge
-
Wavered flake termination
-
Broad flake initiation
-
Feathered terminations on long flakes
-
Low frequency of step or hinge termination
-
Flat flake trajectory
-
Thin flakes
-
Overshots are possible, but are seldom prominent
Indirect percussion (by cylindrical or peg punch)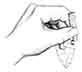
-
Usually to produce blades from cores
-
Lip initiation on blades
-
Biface edges tend to stay in a plane
-
Broad flake initiation
-
Feathered flake termination
-
Thin flakes at late stage
Pressure (by antler)
-
Isolated spur platforms
-
Light platform grinding
-
Small step terminations
-
Selective flake patterning common
-
Subdued bulb of force
-
Tight flake spacing possible
Pressure (by copper)
-
Continuous platforms
-
Ground platforms
-
Serial flake patterning common
-
Prominent bulb of force
-
Tight flake spacing is possible
